Azure Portal: 7 Powerful Features You Must Master Today
Welcome to the ultimate guide on the Azure Portal—a dynamic, feature-rich gateway to Microsoft’s cloud ecosystem. Whether you’re a beginner or a seasoned pro, mastering this platform is essential for efficient cloud management. Let’s dive in.
What Is the Azure Portal?

The Azure Portal is Microsoft’s web-based interface for managing cloud services, resources, and subscriptions within the Azure environment. It provides a centralized dashboard where users can deploy, monitor, and manage virtual machines, storage accounts, networking components, databases, and more—all through an intuitive graphical user interface (GUI).
Core Definition and Purpose
At its heart, the Azure Portal serves as the command center for Azure cloud operations. It allows administrators, developers, and IT professionals to interact with Azure services without needing deep command-line expertise. This makes it ideal for teams looking to streamline cloud workflows with minimal learning curves.
- Acts as a single entry point for all Azure services
- Supports role-based access control (RBAC) for secure collaboration
- Enables real-time monitoring and alerts
How It Compares to CLI and PowerShell
While tools like Azure CLI and Azure PowerShell offer powerful scripting capabilities, the Azure Portal excels in accessibility and visualization. For instance, creating a virtual machine via CLI requires precise syntax, whereas the portal guides users step-by-step through configuration options.
“The Azure Portal democratizes cloud computing by making complex infrastructure tasks approachable for non-developers.” — Microsoft Azure Documentation
However, for automation and large-scale deployments, CLI and PowerShell remain superior. The portal is best used for exploration, troubleshooting, and initial setup.
Key Features of the Azure Portal
The Azure Portal isn’t just a dashboard—it’s a comprehensive toolkit packed with features designed to enhance productivity, security, and scalability. From resource deployment to cost tracking, every function is built with enterprise needs in mind.
Resource Management and Deployment
One of the most powerful aspects of the Azure Portal is its ability to deploy and manage resources seamlessly. Users can launch virtual machines, create storage accounts, configure app services, and even deploy entire architectures using templates.
- Drag-and-drop interface for building architectures
- Integration with Azure Resource Manager (ARM) templates
- Support for third-party marketplace solutions
For example, deploying a WordPress site can be done in minutes using pre-configured solutions from the Azure Marketplace, accessible directly through the portal.
Monitoring and Diagnostics
The portal integrates deeply with Azure Monitor, providing real-time insights into application performance, system health, and network traffic. Users can set up custom dashboards, view logs, and receive alerts based on predefined thresholds.
- Live metrics for CPU, memory, and disk usage
- Application Insights for end-to-end transaction tracing
- Log Analytics for querying operational data
This level of observability ensures that issues are detected and resolved before they impact end users.
Security and Identity Management
Security is baked into the Azure Portal through integration with Azure Active Directory (Azure AD), Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), and Conditional Access policies. Administrators can define granular permissions and audit user activity across the environment.
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) for fine-grained permissions
- Identity Protection for detecting risky sign-ins
- Secure Score to assess and improve security posture
These tools help organizations meet compliance standards such as GDPR, HIPAA, and ISO 27001.
Navigating the Azure Portal Interface
Understanding the layout of the Azure Portal is crucial for maximizing efficiency. The interface is designed to be intuitive, but its depth means new users may feel overwhelmed at first. Let’s break down the key components.
Dashboard and Customization
Upon logging in, users land on a customizable dashboard. This space can be tailored to display tiles for frequently used services, cost summaries, performance charts, and alert feeds.
- Add, resize, or remove tiles based on workflow needs
- Save multiple dashboard layouts for different roles (e.g., DevOps vs. Finance)
- Pin resources for quick access
For instance, a database administrator might pin SQL databases and performance monitors, while a billing manager focuses on cost analysis widgets.
Search and Service Navigation
The global search bar at the top of the portal is one of its most underutilized yet powerful tools. Typing any service name—like “Virtual Machines” or “Blob Storage”—instantly navigates to the relevant section.
- Auto-suggests services, resources, and documentation
- Filters results by resource type, subscription, or region
- Supports natural language queries in preview mode
This feature drastically reduces navigation time, especially in environments with hundreds of resources.
Subscription and Tenant Management
The portal allows users to switch between subscriptions and Azure AD tenants effortlessly. This is particularly useful for consultants or MSPs managing multiple clients.
- Select active directory context from the top-right menu
- View spending per subscription with cost analysis tools
- Apply policies across subscriptions using Azure Policy
Understanding tenant boundaries is critical for maintaining security and compliance across organizational units.
Managing Resources via the Azure Portal
Effective resource management is the backbone of any successful cloud strategy. The Azure Portal provides a unified experience for provisioning, configuring, and retiring cloud assets.
Creating and Configuring Virtual Machines
Deploying a virtual machine (VM) in the Azure Portal is straightforward. Users select the VM type, choose an image (Windows, Linux, or custom), configure size, networking, and storage, then deploy with a few clicks.
- Choose from hundreds of pre-built images in the marketplace
- Automate setup with cloud-init or custom scripts
- Enable auto-shutdown to reduce costs
Detailed pricing calculators are embedded within the creation wizard, helping users estimate monthly costs before deployment.
Working with Storage Accounts
Storage accounts are foundational in Azure, supporting blobs, files, queues, and tables. The portal provides a clean interface for managing access tiers, replication settings, and shared access signatures (SAS).
- Switch between hot, cool, and archive tiers based on usage patterns
- Configure CORS rules for web applications
- Enable soft delete to recover accidentally removed data
For developers, the portal also includes a built-in storage explorer for browsing blob containers and uploading files directly.
Networking and Virtual Networks (VNet)
Networking in Azure revolves around Virtual Networks (VNets), which the portal simplifies through visual design tools. Users can define subnets, route tables, and network security groups (NSGs) with ease.
- Visualize network topology with Network Watcher
- Set up site-to-site or point-to-site VPNs
- Integrate with Azure DNS and Traffic Manager
The portal also supports hybrid scenarios, allowing seamless connection between on-premises data centers and Azure VNets via ExpressRoute or VPN Gateway.
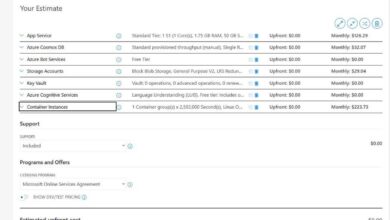
Cost Management and Optimization in the Azure Portal
One of the biggest challenges in cloud computing is controlling costs. The Azure Portal offers robust tools to track, analyze, and optimize spending across your environment.
Understanding the Cost Management Dashboard
The Cost Management + Billing section provides a comprehensive view of your Azure expenditure. You can filter costs by date range, service, resource group, or tag.
- View daily and monthly trends
- Compare actual spend against budgets
- Download detailed reports in CSV format
This transparency helps finance teams forecast budgets and identify underutilized resources.
Setting Up Budgets and Alerts
To prevent cost overruns, the portal allows users to define budgets with threshold-based alerts. For example, you can set a monthly budget of $500 and receive email notifications when spending hits 80% and 100%.
- Create budgets at subscription or resource group level
- Configure action groups for automated responses (e.g., trigger a Logic App)
- Use anomaly detection to flag unexpected spikes
These proactive measures ensure financial accountability across teams.
Identifying and Reducing Waste
The portal includes a feature called Cost Analysis that highlights idle or underused resources. Common examples include unattached disks, oversized VMs, and unused public IPs.
- Use the ‘Recommendations’ tab in Advisor for optimization tips
- Right-size VMs based on historical CPU usage
- Delete orphaned snapshots and backups
According to Microsoft, organizations that actively use Cost Management tools save an average of 20–30% on their cloud bills.
Security and Compliance Tools in the Azure Portal
Security is not an afterthought in Azure—it’s integrated at every level. The portal provides centralized access to tools that help protect data, detect threats, and maintain regulatory compliance.
Azure Security Center (Now Part of Microsoft Defender for Cloud)
Microsoft Defender for Cloud (formerly Azure Security Center) offers unified security management and advanced threat protection across hybrid cloud workloads.
- Provides a Secure Score to measure security posture
- Automatically detects vulnerabilities in OS and configurations
- Offers just-in-time VM access to minimize exposure
It continuously monitors resources and recommends actions like enabling disk encryption or applying missing patches.
Azure Policy and Governance
Azure Policy enables organizations to enforce organizational standards and assess compliance at scale. Policies can be applied to subscriptions or management groups.
- Enforce naming conventions for resources
- Restrict deployment to approved regions
- Ensure all storage accounts have encryption enabled
For example, a policy can automatically deny the creation of public blob storage containers, reducing the risk of data leaks.
Audit Logs and Activity Tracking
The Azure Portal includes a robust logging system through Azure Monitor and the Activity Log. Every action—whether it’s creating a VM or changing a firewall rule—is recorded.
- Access logs via the ‘Monitor’ section
- Stream logs to Event Hubs or export to SIEM tools
- Filter by user, operation, or time range
These logs are essential for forensic analysis, compliance audits, and identifying unauthorized changes.
Automation and DevOps Integration with the Azure Portal
While the Azure Portal is GUI-driven, it seamlessly integrates with automation and DevOps practices, bridging the gap between manual operations and code-based infrastructure.
Using ARM Templates from the Portal
Azure Resource Manager (ARM) templates allow infrastructure to be defined as code. The portal supports exporting existing resource configurations as ARM templates, enabling version control and repeatable deployments.
- Export a resource group’s configuration as JSON
- Deploy templates via the portal’s ‘Deploy a custom template’ option
- Integrate with GitHub or Azure DevOps for CI/CD pipelines
This capability is invaluable for teams practicing Infrastructure as Code (IaC).
Integration with Azure DevOps and GitHub
The portal links directly to Azure DevOps and GitHub repositories, allowing developers to trigger deployments from code commits. For example, pushing code to a GitHub branch can automatically deploy a web app via Azure Pipelines.
- Set up continuous deployment for App Services
- Use deployment slots for zero-downtime updates
- Monitor build and release status within the portal
This tight integration accelerates development cycles and improves deployment reliability.
Logic Apps and Workflow Automation
Azure Logic Apps, accessible through the portal, enable no-code automation of business processes. Users can create workflows that connect Azure services, SaaS apps, and on-premises systems.
- Trigger actions based on events (e.g., new blob upload)
- Send emails, post to Teams, or update databases
- Use built-in connectors for Office 365, Salesforce, and more
For example, a workflow can automatically archive files older than 90 days to lower-cost storage.
Best Practices for Using the Azure Portal
To get the most out of the Azure Portal, it’s important to follow proven best practices that enhance security, efficiency, and scalability.
Organize Resources with Tags and Resource Groups
Tags and resource groups are fundamental for organizing and managing Azure resources. Tags allow metadata-based filtering (e.g., ‘Environment=Production’, ‘Owner=Finance’), while resource groups enable bulk operations.
- Use consistent tagging policies across teams
- Group related resources (e.g., web server, DB, cache) in one resource group
- Apply tags for cost allocation and reporting
This structure simplifies management and improves accountability.
Leverage the Azure Advisor
Azure Advisor is a personalized guidance engine built into the portal. It analyzes your usage patterns and provides actionable recommendations across five pillars: cost, performance, high availability, security, and operational excellence.
- Follow cost-saving suggestions like resizing underutilized VMs
- Improve performance by enabling caching or upgrading SKUs
- Enhance security with MFA and disk encryption
Regularly reviewing Advisor recommendations can lead to significant improvements in efficiency and resilience.
Enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Security starts with identity. Enabling MFA for all users—especially administrators—is one of the most effective ways to prevent unauthorized access.
- Configure MFA through Azure AD in the portal
- Use conditional access policies to enforce MFA for sensitive operations
- Register multiple authentication methods (phone, app, token)
According to Microsoft, MFA blocks over 99.9% of account compromise attacks.
What is the Azure Portal used for?
The Azure Portal is used to manage all aspects of Microsoft Azure cloud services, including deploying virtual machines, managing storage, configuring networks, monitoring performance, controlling costs, and enforcing security policies—all through a web-based interface.
Is the Azure Portal free to use?
Yes, access to the Azure Portal itself is free. However, the cloud resources you create and manage through it (like VMs, storage, and bandwidth) incur charges based on usage. You can use the Azure Pricing Calculator to estimate costs.
How do I secure my Azure Portal access?
Secure your Azure Portal access by enabling Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), using Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) to limit permissions, applying Conditional Access policies, and regularly auditing sign-in logs through Azure AD.
Can I automate tasks in the Azure Portal?
Yes, while the portal is GUI-based, it supports automation through ARM templates, Azure CLI, PowerShell, and integration with Azure DevOps and Logic Apps. You can also export configurations as code for repeatable deployments.
What is the difference between Azure Portal and Azure CLI?
The Azure Portal provides a visual, user-friendly interface ideal for beginners and interactive management. Azure CLI is a command-line tool better suited for scripting, automation, and bulk operations. Both can manage the same resources but serve different use cases.
The Azure Portal is far more than just a dashboard—it’s a comprehensive cloud management platform that empowers organizations to build, secure, and optimize their digital infrastructure. From intuitive navigation to advanced automation and cost controls, mastering its features is essential for anyone working with Microsoft Azure. By leveraging tools like Advisor, Security Center, and Cost Management, teams can achieve greater efficiency, compliance, and resilience. Whether you’re deploying your first VM or managing a global enterprise environment, the Azure Portal provides the visibility and control needed to succeed in the cloud era.
Further Reading: