Azure Apps: 7 Ultimate Power Tips for Dominating Cloud Development
Welcome to the world of Azure apps, where innovation meets scalability. Whether you’re building a simple web app or orchestrating complex microservices, Microsoft Azure offers a robust, flexible, and secure environment to bring your vision to life—fast, efficiently, and globally.
What Are Azure Apps and Why They Matter

Azure apps refer to applications developed, deployed, and managed using Microsoft Azure’s cloud computing platform. These apps span web apps, mobile backends, APIs, serverless functions, and containerized services, all hosted in the cloud. Azure apps empower businesses to scale on demand, reduce infrastructure costs, and accelerate time-to-market.
Defining Azure Apps in Modern Development
Azure apps are not just hosted applications—they represent a complete ecosystem for building, testing, deploying, and monitoring software in the cloud. From simple static websites to AI-powered enterprise systems, Azure apps leverage cloud-native principles to deliver performance, reliability, and agility.
- Azure App Service hosts web and mobile apps with built-in scalability.
- Azure Functions enables event-driven, serverless computing.
- Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) manages containerized apps at scale.
These components allow developers to focus on code, not infrastructure.
Core Benefits of Building Azure Apps
Developing with Azure apps offers unmatched advantages in today’s competitive tech landscape. With global data centers, enterprise-grade security, and seamless integration with Microsoft 365 and DevOps tools, Azure apps provide a future-proof foundation.
- Scalability: Automatically scale up or out based on traffic.
- Cost Efficiency: Pay only for what you use with flexible pricing models.
- Security & Compliance: Built-in compliance with GDPR, HIPAA, ISO, and more.
“Azure is not just a cloud platform—it’s a complete developer ecosystem.” — Microsoft Azure Documentation
Key Services Behind Azure Apps
The strength of Azure apps lies in the breadth and depth of services that support them. From deployment platforms to backend services, Azure offers a modular, composable architecture that fits any development need.
Azure App Service: The Heart of Web Apps
Azure App Service is the cornerstone for hosting web applications, REST APIs, and mobile backends. It supports multiple languages—.NET, Node.js, Python, Java, PHP—and integrates seamlessly with CI/CD pipelines.
- Supports both Windows and Linux environments.
- Enables custom domains and SSL certificates.
- Integrates with Azure DevOps, GitHub, and Bitbucket for automated deployments.
With features like staging slots and traffic routing, App Service allows zero-downtime deployments—critical for enterprise-grade Azure apps.
Azure Functions: Serverless Power for Event-Driven Apps
Azure Functions lets you run small pieces of code (functions) in response to events—without managing servers. This is ideal for background processing, data transformation, or integrating microservices within Azure apps.
- Triggers include HTTP requests, timers, queues, and blob storage events.
- Supports C#, JavaScript, Python, PowerShell, and more.
- Consumption plan charges only when code runs, reducing costs.
For example, an Azure Function can automatically resize images uploaded to Blob Storage—perfect for media-heavy Azure apps.
Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS): Orchestrating Containerized Apps
For complex, scalable applications, AKS provides managed Kubernetes clusters to deploy, scale, and manage containerized Azure apps. It abstracts away cluster management, letting teams focus on application logic.
- Automated upgrades and health monitoring.
- Integration with Azure Monitor and Azure Active Directory.
- Supports hybrid deployments with Azure Arc.
AKS is ideal for microservices architectures, where different parts of an app run independently but communicate via APIs—common in modern Azure apps.
Building Scalable Azure Apps: Best Practices
Creating scalable Azure apps requires more than just deploying code. It demands thoughtful architecture, performance optimization, and proactive monitoring. Here’s how to build Azure apps that grow with your user base.
Design for Scalability from Day One
Scalability should be a core design principle, not an afterthought. Azure apps must handle traffic spikes without degradation in performance.
- Use auto-scaling rules in App Service or VM Scale Sets.
- Offload heavy tasks to Azure Functions or Logic Apps.
- Leverage Azure CDN for static content delivery.
For example, a retail app during Black Friday can scale from 100 to 100,000 users seamlessly with proper Azure configuration.
Implement Microservices Architecture
Breaking down monolithic apps into microservices allows independent development, deployment, and scaling. Each service in your Azure apps can be updated without affecting others.
- Use Azure Service Bus or Event Grid for inter-service communication.
- Store service data in dedicated databases (e.g., Cosmos DB, SQL Database).
- Secure APIs with Azure API Management.
This modular approach improves fault tolerance and accelerates development cycles in large Azure apps.
Optimize Performance with Caching and CDNs
Speed is critical for user retention. Azure apps can leverage Azure Cache for Redis and Azure CDN to reduce latency and improve response times.
- Cache frequently accessed data (e.g., user sessions, product catalogs).
- Use CDN to serve images, CSS, and JavaScript from edge locations.
- Enable compression and minification in App Service.
These optimizations can reduce page load times by up to 60%, significantly enhancing user experience in Azure apps.
Security and Compliance in Azure Apps
Security is non-negotiable in cloud development. Azure apps must be protected against threats while complying with industry regulations. Azure provides a comprehensive security framework to achieve this.
Secure Authentication and Authorization
Protecting access to Azure apps starts with robust identity management. Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) is the backbone of secure authentication.
- Enable single sign-on (SSO) across applications.
- Enforce multi-factor authentication (MFA) for users.
- Use managed identities to avoid storing credentials in code.
For example, an internal Azure app can require MFA and conditional access policies based on user location or device compliance.
Data Protection and Encryption
Data breaches can be catastrophic. Azure apps must encrypt data at rest and in transit using industry-standard protocols.
- Enable Transparent Data Encryption (TDE) for Azure SQL Database.
- Use Azure Key Vault to manage encryption keys securely.
- Apply role-based access control (RBAC) to limit data access.
Azure Key Vault integrates seamlessly with App Service and Functions, ensuring secrets are never hardcoded.
Compliance and Governance
Azure apps in regulated industries (healthcare, finance, government) must adhere to strict compliance standards. Azure offers built-in compliance controls for major frameworks.
- GDPR for data privacy in the EU.
- HIPAA for healthcare data in the US.
- ISO 27001 for information security management.
Use Azure Policy to enforce organizational rules—like requiring all Azure apps to use HTTPS or disabling public IP addresses.
DevOps and CI/CD for Azure Apps
Modern Azure apps thrive on automation. Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) pipelines ensure rapid, reliable releases with minimal manual intervention.
Setting Up CI/CD with Azure DevOps
Azure DevOps provides a complete suite for planning, building, testing, and deploying Azure apps. Pipelines can be configured to trigger on every code commit.
- Create build pipelines to compile and test code.
- Set up release pipelines to deploy to staging and production.
- Integrate unit tests and code coverage reports.
For example, a pull request to the main branch can automatically trigger a build, run tests, and deploy to a test environment—ensuring quality before production.
Using GitHub Actions for Azure App Deployment
For teams using GitHub, GitHub Actions offers powerful automation directly in the repository. You can deploy Azure apps with custom workflows.
- Trigger deployments on push to specific branches.
- Use pre-built actions like
azure/webapps-deploy. - Secure secrets using GitHub’s secret management.
This integration allows open-source and hybrid teams to manage Azure apps efficiently without switching platforms.
Monitoring and Feedback Loops
CI/CD isn’t just about deployment—it’s about feedback. Azure Monitor and Application Insights provide real-time insights into Azure apps’ performance and errors.
- Track request rates, response times, and failure counts.
- Set up alerts for anomalies (e.g., high CPU, 500 errors).
- Use logs to debug issues in production.
These tools close the loop, enabling teams to detect and fix issues before users are impacted.
Cost Management for Azure Apps
While the cloud offers flexibility, costs can spiral without proper oversight. Managing expenses is crucial for sustainable Azure apps.
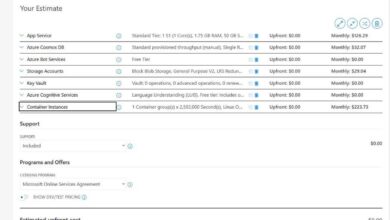
Understanding Azure Pricing Models
Azure offers multiple pricing tiers: pay-as-you-go, reserved instances, and free tiers. Choosing the right model impacts cost efficiency.
- App Service has Free, Basic, Standard, and Premium tiers.
- Functions use a consumption model—pay per execution.
- AKS charges only for VMs and storage, not the control plane.
For example, a startup might start with the Free tier and scale to Premium as traffic grows.
Optimizing Resource Usage
Right-sizing resources prevents over-provisioning. Many Azure apps run on oversized plans unnecessarily.
- Use Azure Advisor to get cost-saving recommendations.
- Scale down during off-peak hours (e.g., dev environments at night).
- Delete unused resources like old storage accounts or test apps.
One company reduced Azure costs by 40% simply by shutting down non-production environments after business hours.
Using Azure Cost Management Tools
Azure Cost Management + Billing provides dashboards, budgets, and reports to track spending across subscriptions.
- Set monthly budgets with email alerts.
- Tag resources by project, team, or environment for cost allocation.
- Analyze trends and forecast future spending.
These tools empower teams to take ownership of their Azure apps’ financial impact.
Real-World Use Cases of Azure Apps
Theoretical knowledge is valuable, but real-world examples show the true power of Azure apps. Let’s explore how organizations leverage Azure to solve business challenges.
E-Commerce Platform on Azure App Service
A global retailer migrated its e-commerce site to Azure App Service, improving uptime from 95% to 99.95%. They used deployment slots to test new features and rolled back instantly if issues arose.
- Integrated with Azure SQL Database for product inventory.
- Used Azure CDN to deliver product images globally.
- Leveraged Application Insights to monitor checkout performance.
The result? A 30% increase in conversion rates and faster load times worldwide.
IoT Data Processing with Azure Functions
A manufacturing company deployed sensors across its factory floor, sending data to Azure IoT Hub. Azure Functions processed incoming telemetry, triggering alerts for equipment anomalies.
- Functions wrote data to Azure Cosmos DB for real-time analytics.
- Sent SMS alerts via Twilio integration when thresholds were exceeded.
- Used Durable Functions for long-running workflows.
This predictive maintenance system reduced downtime by 25%—a direct impact from intelligent Azure apps.
Hybrid Cloud App with AKS and On-Premises Systems
A financial institution runs core banking systems on-premises but built a customer portal using AKS. Azure Arc enabled management of both environments from a single pane.
- APIs exposed on-prem data securely via Azure API Management.
- Used Azure AD for unified authentication.
- Monitored everything with Azure Monitor.
This hybrid approach allowed innovation without replacing legacy systems—showcasing Azure apps’ flexibility.
Future Trends Shaping Azure Apps
The cloud landscape is evolving rapidly. Staying ahead means understanding the trends that will shape the next generation of Azure apps.
AI Integration in Azure Apps
Microsoft is embedding AI across Azure services. Developers can now add cognitive capabilities—like vision, language, and decision-making—to Azure apps with minimal code.
- Azure OpenAI Service brings GPT models to apps for chatbots and content generation.
- Computer Vision API analyzes images uploaded to apps.
- Predictive models in Azure Machine Learning optimize business processes.
For example, a support app can use AI to categorize tickets and suggest responses—reducing resolution time.
Edge Computing with Azure IoT Edge
As latency-sensitive applications grow, processing data closer to the source becomes critical. Azure IoT Edge allows Azure apps to run on edge devices.
- Run AI models on cameras, gateways, or industrial machines.
- Sync data with the cloud when connectivity allows.
- Reduce bandwidth costs and improve responsiveness.
This is transforming industries like healthcare, where real-time analysis of medical devices can save lives.
Sustainable Cloud Development
Sustainability is becoming a key metric. Azure is committed to carbon neutrality, and developers can now optimize Azure apps for energy efficiency.
- Use regions powered by renewable energy.
- Optimize code and queries to reduce compute time.
- Leverage Azure’s Carbon Impact dashboard to measure footprint.
Green Azure apps aren’t just good for the planet—they appeal to eco-conscious customers and investors.
Getting Started with Your First Azure App
Ready to build your first Azure app? The process is straightforward, even for beginners. Microsoft provides extensive documentation, free credits, and sandbox environments.
Step-by-Step: Deploy a Web App in Azure
Follow these steps to deploy a simple web app using Azure App Service:
- Sign up for a free Azure account at azure.microsoft.com.
- Create a new App Service resource in the Azure portal.
- Choose a runtime stack (e.g., Node.js, .NET).
- Deploy code via GitHub, local Git, or ZIP upload.
- Access your app at
yourapp.azurewebsites.net.
You’ll have a live Azure app in under 10 minutes.
Leveraging Azure Free Tier and Credits
Azure offers a free tier with 12 months of popular services and $200 credit for new users. This is perfect for learning and prototyping Azure apps.
- Free services include App Service, Functions, Cosmos DB, and more.
- Credits can be used for any paid service.
- No upfront cost or credit card required in some cases.
Explore Azure Free Account to get started risk-free.
Learning Resources and Communities
Microsoft Learn offers free, interactive modules on building Azure apps. From beginner to expert, there’s a path for everyone.
- Complete learning paths like “Develop Azure compute solutions”.
- Join the Azure community on Stack Overflow and Reddit.
- Attend Microsoft Ignite or local Azure meetups.
Continuous learning ensures your Azure apps stay cutting-edge.
What are Azure apps?
Azure apps are applications built and hosted on Microsoft Azure’s cloud platform. They include web apps, mobile backends, APIs, serverless functions, and containerized services, all designed to scale, secure, and integrate seamlessly with other Microsoft services.
How much does it cost to run Azure apps?
Costs vary based on services used. Azure offers a free tier and $200 credit for new users. App Service starts at $13/month, Functions charge per execution, and AKS has no control plane fee. Use the Azure Pricing Calculator to estimate costs.
Can I deploy existing apps to Azure?
Yes. Azure supports migration of on-premises and legacy apps. Tools like Azure Migrate assess compatibility, and App Service allows rehosting web apps with minimal changes.
How do I secure my Azure apps?
Use Azure Active Directory for authentication, Azure Key Vault for secrets, and enable HTTPS. Apply role-based access control (RBAC) and monitor with Azure Security Center.
What’s the difference between Azure App Service and Azure Functions?
Azure App Service hosts full web applications and APIs, while Azure Functions is for event-driven, serverless code snippets. App Service is ideal for long-running apps; Functions for short, triggered tasks.
Building powerful Azure apps is no longer a luxury—it’s a necessity in today’s digital-first world. From scalable web platforms to intelligent, AI-driven systems, Azure provides the tools, security, and global reach to turn ideas into reality. By leveraging services like App Service, Functions, and AKS, adopting DevOps practices, and optimizing for cost and performance, developers and organizations can create applications that are not only robust but future-ready. As cloud technology evolves, staying informed about trends like AI integration, edge computing, and sustainability will ensure your Azure apps remain competitive and impactful. Whether you’re just starting or scaling an enterprise solution, the Azure ecosystem offers a powerful foundation to innovate, grow, and succeed.
Further Reading: